|
 A
coffee cup* could hold approximately 700,000 of NVE’s 1.1 millimeter
square ADL-Series magnetic switches. A
coffee cup* could hold approximately 700,000 of NVE’s 1.1 millimeter
square ADL-Series magnetic switches.
*Although they’re quite rugged, we don’t recommend storing our parts
in coffee cups.
More Fun Facts > |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Application
Corner |
|
|
Two-Wire
Magnetic Proximity Sensor
Two-wire sensors are common in industrial control to simplify wiring. But for
many sensors, competing constraints make designing two-wire interface circuitry
tricky.
Two wire interfaces need to operate over a wide power supply range.
With the sensor off, the circuit must draw a minimal residual current, typically
in the range of one milliamp. With the sensor on, the circuit must provide enough
current to drive a significant load such as a motor or solenoid. Minimum holding
current is another design constraint.
NVE’s ADL-Series sensors are perfect for two-wire applications, because their
low supply voltage and low quiescent current provide plenty of design margin.
Here’s a simple reference circuit:
And here’s a demonstration:
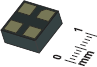 In
addition to their impressive electrical specifications, ADL-Series sensors feature
precise magnetic operate points and an ultraminiature 1.1 millimeter package. In
addition to their impressive electrical specifications, ADL-Series sensors feature
precise magnetic operate points and an ultraminiature 1.1 millimeter package.
Standard ADL-Series magnetic operate points are 20 and 28 oersteds, with
other ranges available by special order.

|
 |
|
|
New
Video |
|
|
Gear
Tooth Sensor Demonstration
NVE Vice President for Sensors Jay Brown demonstrates the extraordinary wide air-gap
range of NVE's unique GMR gear tooth sensors.
The demonstration shows the operation of ABL-Series analog gear-tooth sensors
(both single and dual bridge) and AKL-Series digital gear-tooth sensors.
GT Sensor™ features include:
• Wide airgap tolerance
• DC (zero speed) operation
• Precise spacing between sensor elements
• Excellent performance over temperature and voltage
ABL-Series analog sensors provide sinusoidal outputs with one cycle per tooth.
Dual bridge analog sensors have two out-of-phase outputs for determining direction.
AKL-Series digital sensors include signal processing to provide a 50% duty cycle
digital modulated current signal.
The demonstration shows a gear driven by a motor with a micrometer adjustment
to change the air gap between the sensor and gear. This demonstrates the wide
airgap range accommodated by GT sensors—a range of 5 millimeters or
more.
|
|







